UNITED NATIONS (AP) — The U.N. Security Council approved a resolution Wednesday calling for “urgent and extended humanitarian pauses and corridors throughout the Gaza Strip” after four failed attempts to respond to the Israel-Hamas war.
The vote was 12-0 with the United States, United Kingdom and Russia abstaining.
The final draft watered down language from a “demand” to a “call” for humanitarian pauses. It also watered down a demand for “the immediate and unconditional release of all hostages held by Hamas and other groups."
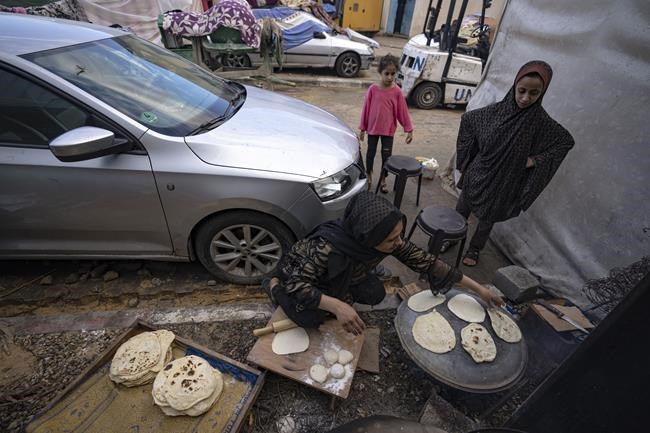
The resolution makes no mention of a cease-fire. It also doesn't refer to Hamas' surprise attack on Israel on Oct. 7, during which the militants killed around 1,200 people and took some 240 others hostage. Nor does it cite Israel’s retaliatory airstrikes and ground offensive in Hamas-ruled Gaza, which Gaza’s health ministry says has killed more than 11,000 Palestinians, two-thirds of them women and children.
Russia proposed an amendment to the resolution before the vote that would have called for durable humanitarian pauses leading to a cease-fire. But it was rejected by a vote of 5-1 with nine abstentions because it failed to get the minimum nine “yes” votes.
But the resolution, sponsored by Malta, did bring the 15 members of the U.N.'s most powerful body together in a first response to the ongoing war that is having catastrophic humanitarian consequence in Gaza.
The resolution asks that “all parties comply with their obligations under international law, notably with regard to the protection of civilians, especially children.”
U.N. Security Council resolutions are legally binding, but in practice many parties choose to ignore the council’s requests for action.
Richard Gowan, U.N. director for the International Crisis Group, said the Security Council has called for cease-fires in wars from the Balkans to Syria “with little or no impact.”
The Security Council, which has the responsibility for maintaining international peace and security, has been paralyzed since the war began by its internal divisions. This is especially the case between China and Russia, which want an immediate cease-fire, and the United States, which has called for humanitarian pauses but objects to any mention of a cease-fire, which its close ally Israel strongly opposes.
The resolution calls for humanitarian pauses and corridors throughout the Gaza Strip for a “sufficient number of days” for unhindered access by the U.N., Red Cross and other aid groups to get water, electricity, fuel, food and medical supplies to all those in need. It says the pauses also should allow for repair of essential infrastructure and enable urgent rescue and recovery efforts.
In the four previous tries for Security Council approval, a Brazil-drafted resolution was vetoed by the United States, a U.S.-drafted resolution was vetoed by Russia and China and two Russian-drafted resolutions failed to get the minimum “yes” votes.
After the fourth failure, frustrated Arab nations turned to the 193-member General Assembly and succeeded in getting wide approval for a resolution calling for a “humanitarian truce” in Gaza meant to lead to a cessation of hostilities between Israel and Hamas.
It was the first United Nations response to the war. But unlike Security Council resolutions, General Assembly resolutions are not legally binding, though they are a barometer of world opinion.
The vote was 120-14 with 45 abstentions. Of the five veto-holding Security Council members, Russia, China and France voted in favor, the United States voted against and Britain abstained.
The General Assembly resolution was adopted Oct. 27, and Israel agreed Nov. 9 to four-hour pauses. But only very limited aid has been delivered to Gaza through the Rafah crossing from Egypt, and a humanitarian catastrophe has been brewing.
The Crisis Group's Gowan said U.S. opposition to a cease-fire “is a gift that keeps on giving for Russia diplomatically.” He said that while many diplomats think Russia is demanding a cease-fire “for largely cynical reasons to make the Americans look bad,” Moscow’s position “is closer to the mainstream of council thinking, and the U.S. looks isolated.”
“A U.N. cease-fire call would embarrass but not really constrain the Israelis,” he told the AP. “But the U.S. clearly feels that even such a symbolic move is too much of a political risk.”
Edith M. Lederer, The Associated Press